Katedrę Mechaniki Budowli i Zastosowań Informatyki powołano 1 kwietnia 2009 roku z połączenia dwóch zakładów: Zakładu Mechaniki Budowli i Zakładu Zastosowań Informatyki w Inżynierii Lądowej.
Główny nurt prac badawczych obu zakładów: ZMB i ZZIwIL obejmuje zakres szeroko rozumianej mechaniki konstrukcji z wykorzystaniem metod numerycznych i technik informatycznych.
Katedra Mechaniki Budowli, z której powstał obecny Zakład Mechaniki Budowli, ma długą i piękną tradycję. Po roku 1945 Katedrą Mechaniki Budowli, przed powstaniem instytutów, kierowali uczeni światowej sławy: profesorowie Witold Wierzbicki, Witold Nowacki i Zbigniew Kączkowski.
Po powstaniu instytutów, tradycję silnego ośrodka naukowego podtrzymywali profesorowie Zbigniew Kączkowski, Zbigniew Mazurkiewicz, Gustaw Rakowski, Zbigniew Reipert, Andrzej Gomuliński i Grzegorz Jemielita. Ci uczeni stworzyli znaną w Polsce szkołę naukową w dziedzinie mechaniki budowli w zakresie: statyki i dynamiki dźwigarów powierzchniowych, teorii płyt i powłok oraz wybranych działów metody elementów skończonych. Ważne prace z zakresu teorii sprężystości płyt są dziełem prof. Grzegorza Jemielity, doktoranta prof. Witolda Nowackiego. Istotne wyniki dotyczące metody elementów skończonych uzyskali prof. Andrzej Gomuliński, prof. Marek Witkowski i dr hab. Wojciech Gilewski. Nowe metody optymalizacji topologicznej konstrukcji były przedmiotem publikacji prof. Tomasza Lewińskiego, dra Grzegorza Dzierżanowskiego i dra Krzysztofa Hetmańskiego. Liczne prace wspólne powstały we współpracy z dr. Sławomirem Czarneckim z ZZI w IL, ze specjalistami spoza Uczelni: z kolegami z IPPT PAN, IBS PAN, Politechniki Krakowskiej oraz z ekspertami z zagranicy.
|
|
Read more...
|
|
Wirtualne modelowanie w projektowaniu |
 |
 |
 |
|
WIRTUALNE MODELOWANIE W PROJEKTOWANIU1
Zbigniew KACPRZYK2
STRESZCZENIE
Przedmiotem pracy jest analiza nauczania zastosowań informatyki na kierunku budownictwo. Oceniono program nauczania na kierunku w zakresie informatyki, porównano z programami nauczania na innych kierunkach technicznych. Krytycznie oceniono niezrozumienie roli komputerowego wspomagania projektowania.
Słowa kluczowe: informatyka, CAD, dydaktyka, budownictwo.
WPROWADZENIE
Przyzwyczailiśmy się do nieustannych zmian w informatyce. Informatyka jest obecna w naszym życiu codziennym, w domu i w pracy. Komputerowe metody analizy konstrukcji w istotny sposób zmieniły rutynowe obliczenia konstruktorów. Przez lata obserwowaliśmy eliminacje tradycyjnego kreślenia i powszechne wykorzystanie rysunku komputerowego. Komputerowe obliczanie wytrzymałościowe konstrukcji i komputerowe kreślenie zmieniło pracę projektantów i mocno obniżyło czasochłonność procesu projektowania. Obecnie znacznie szybciej wykonujemy obliczenia statyczne konstrukcji, często stosujemy bardziej złożone modele obliczeniowe. Też szybciej wykonujemy dokumentacje techniczną, szybciej nanosimy zmiany i modyfikacje, szybciej przygotowujemy kosztorys przedsięwzięcia. Nie jest to koniec zmian bo wiele wskazuje, że prawdziwa rewolucja w projektowaniu dopiero się odbędzie, por. [1]
|
|
Read more...
|
|
Sandwich plates of minimal compliance |
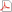 |
 |
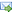 |
Sandwich plates of minimal compliance, S. Czarnecki, M. Kursa, T. Lewiński,
Comput. Methods Appl. Mech. Engrg. 197 (2008) 4866–4881
Read online>>
The subject of the paper is an optimal choice of material parameters characterizing the core layer of sandwichplates within the framework of the conventional plate theory in which the core layer is treated as soft in the in-plane direction. The mathematical description is similar to the Hencky–Reissner model of plates with transverse shear deformation. Here, however, the bending stiffnesses and the transverse shear stiffnesses can be designed independently. The present paper deals only with optimal design of the core layer to make the plate compliance minimal. Two core materials are at our disposal, which leads to the ill-posed problem. To consider it one should relax this problem by admitting composite domains and characterize their overall properties by the homogenization formulae. The numerical approach is based on this relaxed formulation thus making it mesh-independent. The equilibrium problem is solved by the DSG3 finite element method. The optimization results are found with using the convergent updating schemes of the COC method. |
|
Michell structures formed on surfaces of revolution |
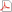 |
 |
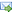 |
Michell structures formed on surfaces of revolution, T. Lewiński,
Structural and Multidisciplinary Optimization 28, 20–30 (2004)
Read online >>
The paper formulates the Michell-like problems for surface gridworks. Particular attention is devoted to the problem of designing the lightest fully stressed gridworks formed on surfaces of revolution. In the examples considered, the gridworks are subjected to torsion. Proof is given that the circular meridian is a minimizer of the weight (or volume) functional of a shell subjected to torsion, thus justifying the original Michell conjecture according to which just the spherical twisting shell is the lightest. The proof is based on the methods of the classical variational calculus and thus can be viewed as elementary. This result is confirmed by a direct comparison of the exact formulae for the weight of a spherical Michell shell with the exact formulae for the weights of optimal conical and cylindrical shells with the same fixed boundaries.
|
|
On refined plate models based on kinematical assumptions |
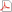 |
 |
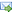 |
On refined plate models based on kinematical assumptions, T. Lewiński, Warsaw
Archive of Applied Mechanics, Volume 57, Number 2, 133-146 (1987)
Read online>>
In the first part of the paper an energy-consistent model for thick, elastic, isotropic plates based upon Jemielita's kinematical hypothesis is proposed. Since no assumptions on stresses are stipulated the model is free of the usual discrepancy between stress and displacement fields, viz. no one of the constitutive equations being violated. The objective of the second part of the paper is to perform a passage from the model obtained to the simplified one which is energy-inconsistent. This latter model proves far-reaching similarities to the first Reissner theory and, on the other hand, when an appropriate change of the function standing for the averaged plate deflection is made, — to the Kelkel's considerations.
|
|
O stosowaniu funkcji wagowych w metodzie czasoprzestrzennych elementów skończonych |
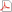 |
 |
 |
|
O stosowaniu funkcji wagowych w metodzie czasoprzestrzennych elementów skończonych, Zbigniew Kacprzyk
Prace Naukowe Politechniki Warszawskiej, seria Budownictwo, z. 85, s. 83-95, 1984
Read online>>
W pracy wyprowadzono pewną metodę numerycznego całkowania równania ruchu. Metoda sformułowana jest tylko w przemieszczeniach. W zależności od przyjetych parametrów otrzymujemy schemat całkowania jawny lub niejawny. Metoda jest w zasadzie uogólnieniem metody czasoprzestrzennych elementów skończonych. Podano kryterium statecznosci metody. Metoda w zależnosci od przyjętych współczynników może być warunkowo lub bezwarunkowo stabilna. Oceniono dokładność rozwiązania i podano algorytm metody. Porównano prezentowaną metodę z metodą Newmarka.
słowa kluczowe: numeryczne całkowanie równań ruchu, metoda czasoprzestrzennych elementów skończonych
On aplication of weighted functions in the space-time finite elements method
A new method of integration of equation of motion, formulated in dispalcements, is presented in the paper. Depending on adopted parameters an explicit or an implicit scheme is obtained. Close relationship is indicated to the space-time finite element method. Stability criterion is given. The method can be conditionally or unconditionally stable, depending on the adopted coefficients. A check on accuracy of the results is made and the algoritm of the method is presented. A comparision is made between the presented method and Newmark's method.
key words: numericat integration of equation of motion, space-time finite elements method |
|
|