Na 3 Kongresie Mechaniki Polskiej oraz 21 międzynarodowej konferencji Metod Komputerowych w Mechanice z Zakładu prezentowane były nastepujące referaty:
 Bołbotowski K., Sokół T. - New method of generating Strut and Tie models using truss topology optimization, Bołbotowski K., Sokół T. - New method of generating Strut and Tie models using truss topology optimization,
Czarnecki S., Czubacki R., Lewiński T., Wawruch P. - The Free Material Design reduced to the Monge-Kantorovich problem,
Czarnecki S., Czubacki R., Wawruch P. - Stress based version of isotropic material design in two dimensions,
Czarnecki S., Czubacki R., Lewiński T. - Topology optimization of spatial continuum structures made of a non-homogeneous material of cubic symmetry,
Czarnecki S., Wawruch P. - Selected problems of numerical analysis of Free Material Design,
Kacprzyk Z., Ostapska-Łuczkowska K. - Available numerical implementations of isogeometric analysis,
Łukasiak T. - HS(ro) – an isotropic material interpolation scheme based on Hashin-Shtrikman variational bounds,
Rozvany G.I.N., Sokół T., Pomezanski V., Gaspar Z. - Extension of Michell's classical (1904) truss topology optimization theory to multiple load conditions, stress and displacement constraints, space (3D) trusses, probabilistic design and discontinuous support conditions,
Sokół T., Rozvany G.I.N. - A new adaptive ground structure method for multi-load spatial Michell structures
|
|
Isotropic Material Design |
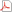 |
 |
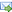 |
Isotropic Material Design
S. Czarnecki
 Computational Methods in Science and Technology, CMST 21(2) 49-64 (2015) Computational Methods in Science and Technology, CMST 21(2) 49-64 (2015)
DOI: 10.12921/cmst.2015.21.02.001
Read online>>
Abstract:
The paper deals with optimal distribution of the bulk and shear moduli minimizing the compliance of an inhomogeneous isotropic elastic 3D body transmitting a given surface loading to a given support. The isoperimetric condition is expressed by the integral of the trace of the Hooke tensor being a linear combination of both moduli. The problem thus formulated is reduced to an auxiliary 3D problem of minimization of a certain stress functional over the stresses being statically admissible. The integrand of the auxiliary functional is a linear combination of the absolute value of the trace and norm of the deviator of the stress field. Thus the integrand is of linear growth. The auxiliary problem is solved numerically by introducing element-wise polynomial approximations of the components of the trial stress fields and imposing satisfaction of the variational equilibrium equations. The under-determinate system of these equations is solved numerically thus reducing the auxiliary problem to an unconstrained problem of nonlinear programming. |
|
The emergence of auxetic material as a result of optimal isotropic design |
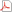 |
 |
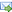 |
The emergence of auxetic material as a result of optimal isotropic design
S. Czarnecki, P. Wawruch
 Phys. Status Solidi B, 1–11 (2015) / DOI 10.1002/pssb.201451733 Phys. Status Solidi B, 1–11 (2015) / DOI 10.1002/pssb.201451733
Read online>>
Abstract:
Using both mathematical and numerical methods, the optimal distributions of material characterized by the Young modulus and Poisson ratio (as well as other moduli of isotropy) maximizing the overall stiffness of an inhomogeneous isotropic elastic 3D body transmitting a given surface loading to a given support are constructed. The overall stiffness of the body is defined as the inverse of the work of external forces on displacements, called here the compliance of the structure. The isoperimetric condition bounds the integral of the trace of the Hooke tensor. It is proved that isotropic composite materials forming the bodies of extremely high stiffness exhibit negative Poisson ratio in large subdomains, which points at the significance of the auxetic material in modern structural design. The obtained results show that the whole range of possible variation of the Poisson ratio is used, from −1 to 1/2, which proves usefulness of the auxetic materials.
|
|
Theoretical Foundations of Civil Engineering, Polish-Ukrainian Transactions, 2014 |
 |
 |
 |
 Uderzenie punktu materialnego w belkę, Jemielita G., Kozyra Z., Theoretical Foundations of Civil Engineering, Polish-Ukrainian Transactions. Ed. by W. Szcześniak, pp. 51-58, Warsaw 2014. Uderzenie punktu materialnego w belkę, Jemielita G., Kozyra Z., Theoretical Foundations of Civil Engineering, Polish-Ukrainian Transactions. Ed. by W. Szcześniak, pp. 51-58, Warsaw 2014.
Streszczenie: W pracy wyznaczono prędkość masy i prędkość punktów materialnych belki w trakcie zderzenia. Wyznaczono też przemieszczenia dynamiczne belki przy zderzeniu elastycznym i nieelastycznym w zależności od przemieszczenia statycznego.
Izotropowe kompozyty periodyczne - homogenizacja struktur I rzedu, Łukasiak T., Theoretical Foundations of Civil Engineering, Polish-Ukrainian Transactions. Ed. by W. Szcześniak, pp. 77-84, Warsaw 2014.
Streszczenie: Materiały kompozytowe w 2D charakteryzuja się z reguły ortotropowymi cechami. Interesującymi, nie tylko z teoretycznego punktu widzenia, są takie kompozyty których makro-właściwości są izotropowe np. stal posiadająca wewnętrzną mikro-strukturę traktowana jest makroskopowo jako ciało izotropowe. W pracy przedstawiono homogenizację kompozytów wykorzystując metodę elementów skończonych.
Parametric Modeling of Space Frame Structures, Kacprzyk Z., Ostapska–Łuczkowska K., Theoretical Foundations of Civil Engineering, Polish-Ukrainian Transactions. Ed. by W. Szcześniak, pp. 167-172, Warsaw 2014.
Abstract: The subject of this paper is a study of different mathematical models of curves and surfaces applied in CAD systems with an aim to identify best modelling approach for a certain design problems. The study is supported by practical examples performed with the use of commercial software. Examples show how modelling approach differs or should differ for different space frames types. For better model efficiency, irrelevant elements are neglected in certain models. |
|
XXIII R-S-P Seminar, Theoretical Foundation of Civil Engineering (23RSP) (TFoCE 2014) |
 |
 |
 |
 XXIII R-S-P Seminar, Theoretical Foundation of Civil Engineering (23RSP) (TFoCE 2014) XXIII R-S-P Seminar, Theoretical Foundation of Civil Engineering (23RSP) (TFoCE 2014)
Edited by Marian Drusa, Ruzica R. Nikolic and Marian Marschalko, Procedia Engineering, Volume 91, Pages 1-492 (2014)
Isogeometric Analysis as a New FEM Formulation - Simple Problems of Steady State Thermal Analysis, Zbigniew Kacprzyk, Katarzyna Ostapska-Łuczkowska, Pages 87-92, doi:10.1016/j.proeng.2014.12.018
Read online>>
Abstract: The subject of this article concerns Isogeometric Analysis as a new formulation within Finite Element Method. Motivation for this new approach was presented together with theoretical foundations of the method. The main subject of the paper is numerical implementation of the method in the Matlab environment. Special focus was put on the new concept of element and new geometry data interpretation in terms of analysis. Object oriented programming was utilized to produce more universal tool for future investigations. Several examples for Poisson's partial differential equation solution were presented. The h-refinement was utilized to show method convergence. Steady state thermal analysis was performed with temperatures and heat flux as boundary conditions. Quick geometry data transfer and mesh refinement from Rhino software with Grasshopper plug-in was also prepared and described in the paper. Finally, authors' conclusions concerning new method were presented and comparison between FEM and IGA was made on the basis of the studied examples.
Keywords: Isogeometric Analysis (IGA); Finite Element Method (FEM); B-spline; NURBS; T-spline; CAD; Computer Aided Engineering ;
Dynamics of Multi-body Mechanical Systems with Unilateral Constraints and Impacts, Artur Zbiciak, Zofia Kozyra, Pages 112-117, doi:10.1016/j.proeng.2014.12.024
Read online>>
Abstract: The paper deals with mathematical description and computer simulation of multi-body dynamical systems with constraints imposed on displacements and velocities. Such mechanical systems contain a finite number of material points, whose motion is limited by unilateral constraints. The mathematical description of the problem, concerning the interaction between material points and unilateral constraints, is presented. The dynamic problem was defined in order to evaluate accelerations of elements and reactions of constraints. Moreover, the impact problem was formulated. The solution of the impact problem determines non-continuous change in velocities of elements and impulses of constraints' reactions.
Keywords: dynamics; non-smooth mechanics; multi-body systems; unilateral constraints; impact; contact; non-linear vibrations ;
Traditional Design versus BIM Based Design, Ireneusz Czmoch, Adam Pękala, Pages 210-215, doi:10.1016/j.proeng.2014.12.048
Read online>>
Abstract:The paper shortly presents the history and development of the traditional design in civil engineering. Next, the idea of Building Information Modelling (BIM) and its practical benefits are described. Main part of the paper is devoted to discussion about what kind of difficulties we may encounter during the implementation of the BIM technology and how they are related to the potential benefits. Case study presents the existing design prepared in BIM technology.
Keywords: traditional design; civil engineering; CAD; BIM
Building Information Modelling – 4D Modelling Technology on the Example of the Reconstruction Stairwell, Zbigniew Kacprzyk, Tomasz Kępa, Pages 226-231, doi:10.1016/j.proeng.2014.12.051
Read online>>
Abstract: Building Information Modelling (BIM) is a process that involves creating, generating, managing and using a digital representations of physical and functional characteristics of building. The use of the term 4D is intended to refer to the fourth dimension: time, i.e. 4D is 3D + schedule (time). The role of 4D BIM is to add a new dimension to 3D CAD or solid modelling—that is, 4D BIM adds a fourth dimension of Time to the 3D Space of CAD solid modelling on computer. In the paper show the project entirely made using 4D BIM
Keywords: Building Information Modelling (BIM); 3D design; CAD; architectural engineering and construction (AEC) software |
|
|




 Bołbotowski K., Sokół T. - New method of generating Strut and Tie models using truss topology optimization,
Bołbotowski K., Sokół T. - New method of generating Strut and Tie models using truss topology optimization, Computational Methods in Science and Technology, CMST 21(2) 49-64 (2015)
Computational Methods in Science and Technology, CMST 21(2) 49-64 (2015)
 Uderzenie punktu materialnego w belkę, Jemielita G., Kozyra Z., Theoretical Foundations of Civil Engineering, Polish-Ukrainian Transactions. Ed. by W. Szcześniak, pp. 51-58, Warsaw 2014.
Uderzenie punktu materialnego w belkę, Jemielita G., Kozyra Z., Theoretical Foundations of Civil Engineering, Polish-Ukrainian Transactions. Ed. by W. Szcześniak, pp. 51-58, Warsaw 2014. XXIII R-S-P Seminar, Theoretical Foundation of Civil Engineering (23RSP) (TFoCE 2014)
XXIII R-S-P Seminar, Theoretical Foundation of Civil Engineering (23RSP) (TFoCE 2014)
